ISI 09-2e Determination of Fibre in Starch by Weight
| 1. Scope |
The method is applicable to native potato and cassava starch
|
LT 1994 Rev. LT 11. Dec. 1997 |
| 2. Principle |
Starch is hydrolyzed and filtered. Fibre defined as non-soluble
impurities are retained, dried and determined by weight.
|
Cornstarches do not filter properly. |
| 3. Apparatus |
3.1 Analytical balance weighing to the nearest 1 mg.
3.2 Shaking boiling water bath. |
|
|
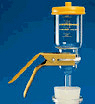
3.3 Büchner funnel or Sartorius 250 ml glass vacuum filter funnel. |
Use a high flux filter. Do not use a glass frit filter support | |
| 4. Reagents |
4.1 Dilute hydrochloric acid 0.1 N
|
|
| 5. Procedure | 100.0 g (w1) sample is slurried in a 1000 ml conical flask with 600 ml acid (4.1) | |
|
Hydrolysis |
Place flask in boiling water bath (3.2) for 30 min | Shake min. until starch is gelatinised |
|
Filtration |
Filter hot on filter (3.3). Flush flask and filter with 100 ml hot water. | Increase hydrolysis parameters if flux too low |
| Dry filter at 105 oC over night - min 12 hours. Weigh filter to nearest 1 mg (m1) | ||
|
Blind |
10.0 g (w0) sample is slurried in a 100 ml conical flask with
60 ml acid (4.1). Hydrolyse and filter as above. Weigh filter to nearest
1 mg (m0)
|
|
| 6. Calculation |
Calculate fibre of sample by averaging results of two samples with two
decimals.
Fibre % = 100 * ((m1 - m0) / (1 - w0 / w1)) / w1 |
|
|
Eventually correct to value on sample dry matter.
|
||
| 7. Notes |
Alternative: Substitute acid with heat stable alpha-amylase. It is
essential to hydrolyse to obtain high flux through filter. Use a filter
holder with a screen filter support or other non-clogging support.
|
|
| 8. References | Similar AOAC method for crude fibre may be applied as more specific for residual plant fibre. | AOAC method detects lignin and cellulose |
| 9. Image |
|
Sartorius filter funnel(min 250 ml) with glass vacuum holder for 47 mm filters with PTFE-coated steel screen filter support |
Comments
Post a Comment